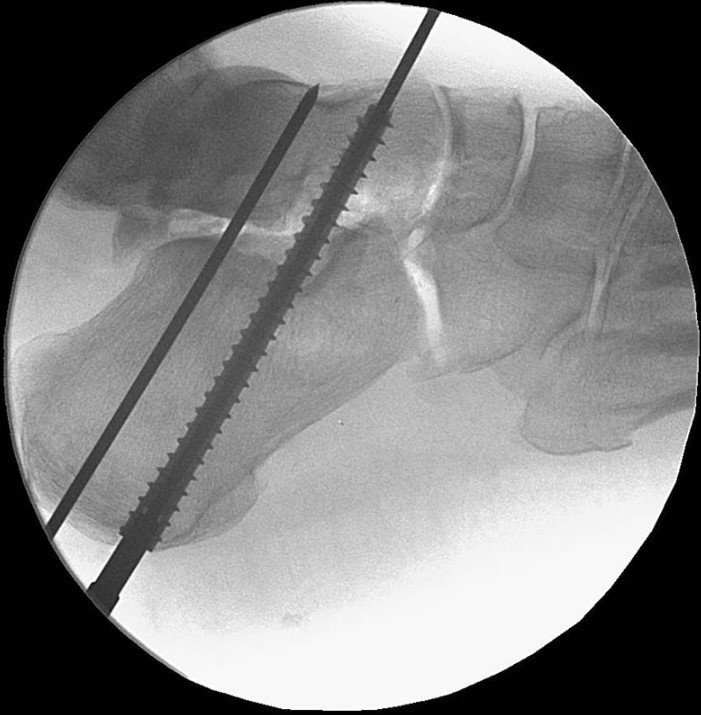
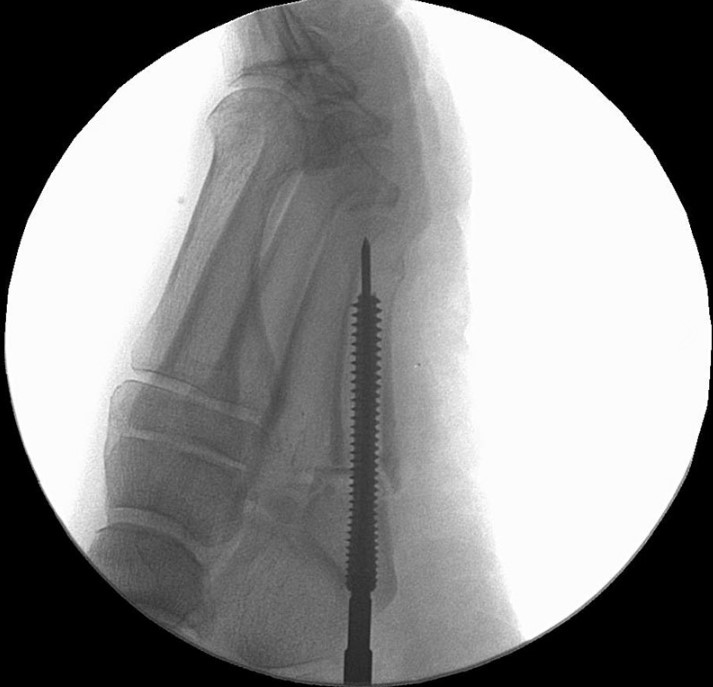
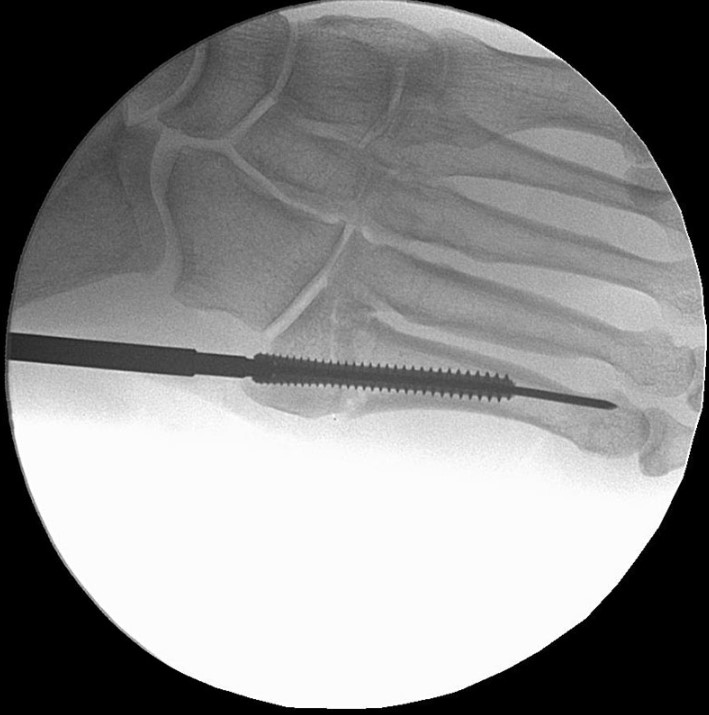
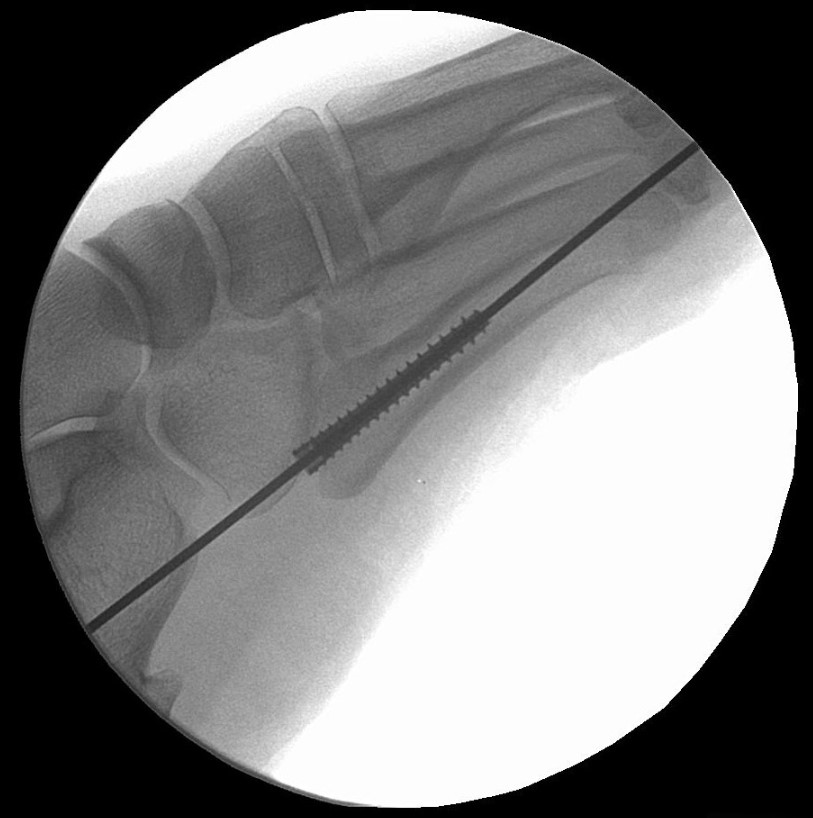
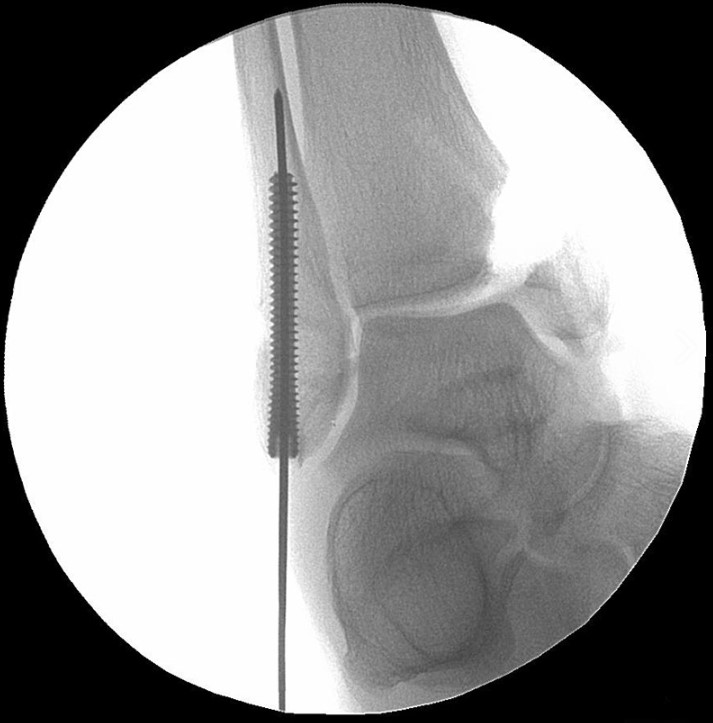
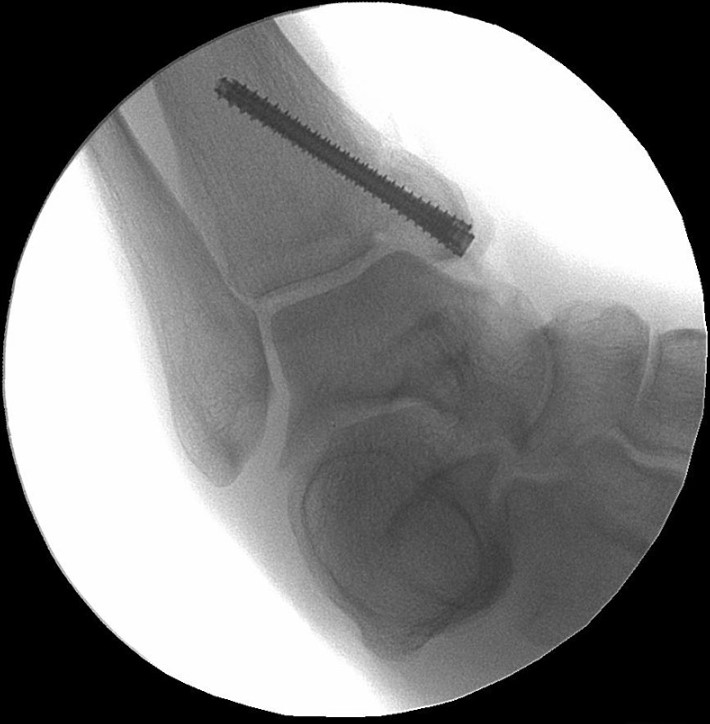
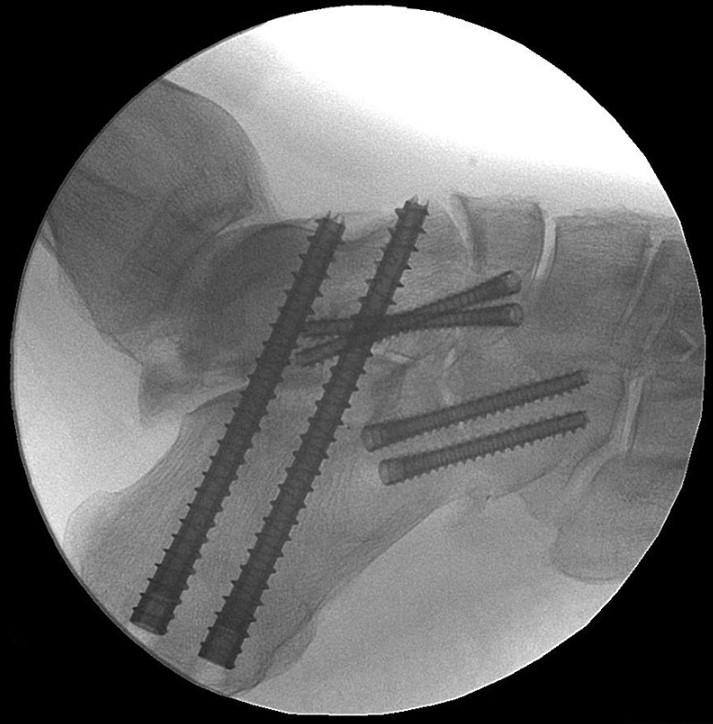
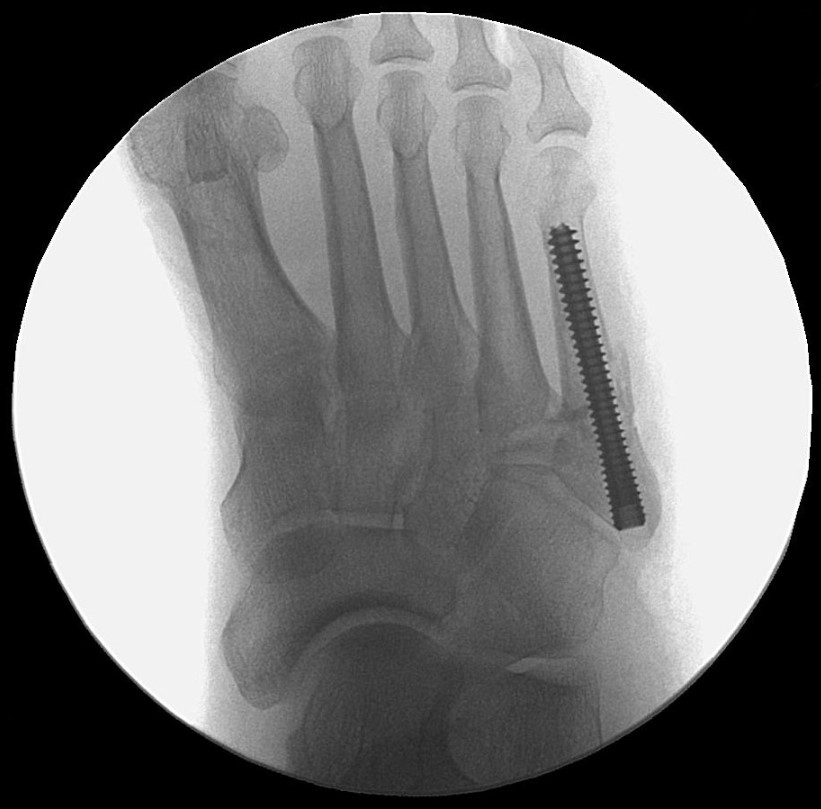
Surgical Technique
Acutrak 2 Headless Compression Screw System
-
SURGICAL TECHNIQUES
DOWNLOADField Guide – Bunions and Forefoot Reconstruction
DOWNLOADSupplemental Use Guide – Calcaneal Osteotomy
DOWNLOADSupplemental Use Guide – Dorsal Scaphoid
DOWNLOADSupplemental Use Guide – Foot and Ankle
DOWNLOADSupplemental Use Guide – Four Corner Fusion
DOWNLOADSupplemental Use Guide – Hand and Wrist
DOWNLOADSupplemental Use Guide – Medial & Lateral Malleolus
DOWNLOADSupplemental Use Guide – Proximal Fifth Metatarsal Fracture
DOWNLOADSupplemental Use Guide – Standard Triple Arthrodesis
DOWNLOADScrew Removal Brochure
DOWNLOADSupplemental Use Guide – Intramedullary Fixation of
Metacarpal Fractures: Antegrade ApproachDOWNLOADSupplemental Use Guide – Intramedullary Fixation of
Metacarpal Fractures: Retrograde ApproachDOWNLOAD -
BROCHURES
A Complete Selection Trimalleolar Fracture Solutions
DOWNLOADA Complete Range of Trusted Hand Solutions
DOWNLOADAcutrak 2 Brochure
DOWNLOADAcutrak Headless Compression Screw Solutions Brochure
DOWNLOADComprehensive Hand Fracture Solutions Brochure
DOWNLOADSolving Flatfoot
DOWNLOADTrimalleolar Fracture Solutions Brochure
DOWNLOAD -
CASE STUDIES
Left Calcaneus Fracture Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF) – Acutrak Headless Compression Screws and Callos Bone Void Filler Case Study
DOWNLOADMedial Double Arthrodesis in the Setting of Advanced Rigid Bilateral Pes Planus Case Study
DOWNLOADRadial Head Fracture Case Study
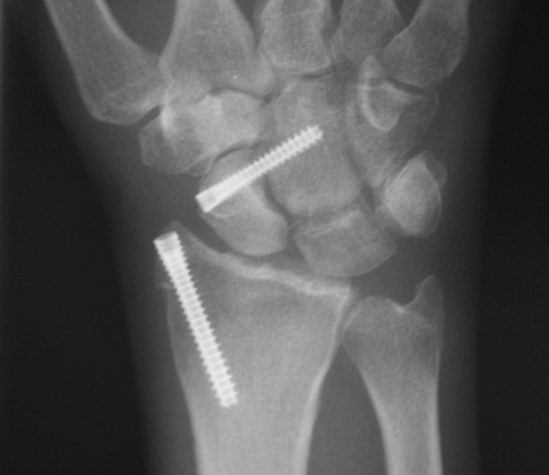
DOWNLOADUse Of Acutrak 2 Headless Compression Screw For Treatment Of Scaphoid Waist Fracture – Ramesh Srinivasan, MD Case Study
DOWNLOAD -
TECHNICAL
Technical Article List
DOWNLOADScrew/Pin Reference Chart
DOWNLOADAcutrak 2 Screw System Value Analysis Resource Guide
DOWNLOADA Heritage of Healing: Acutrak Technology for Headless Compression Screws
DOWNLOADCompression and Insertion Torque Comparison between Acumed Acutrak 2 Mini and Arthrex 3.5 mm Mini Compression FT Headless Compression Screws
DOWNLOADCompression and Insertion Torque Comparison of Acumed to Arthrex Headless Compression Screws
DOWNLOAD
Acutrak 2 Headless Compression Screw System
Product Overview
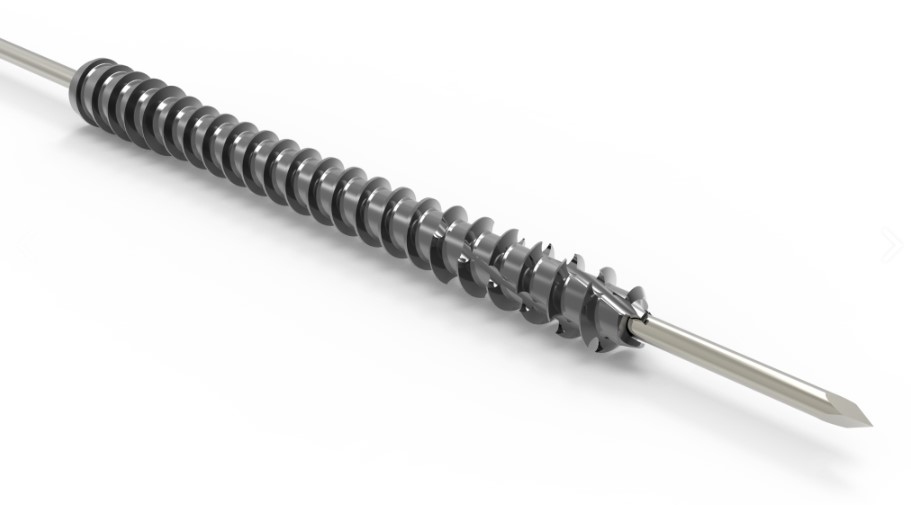
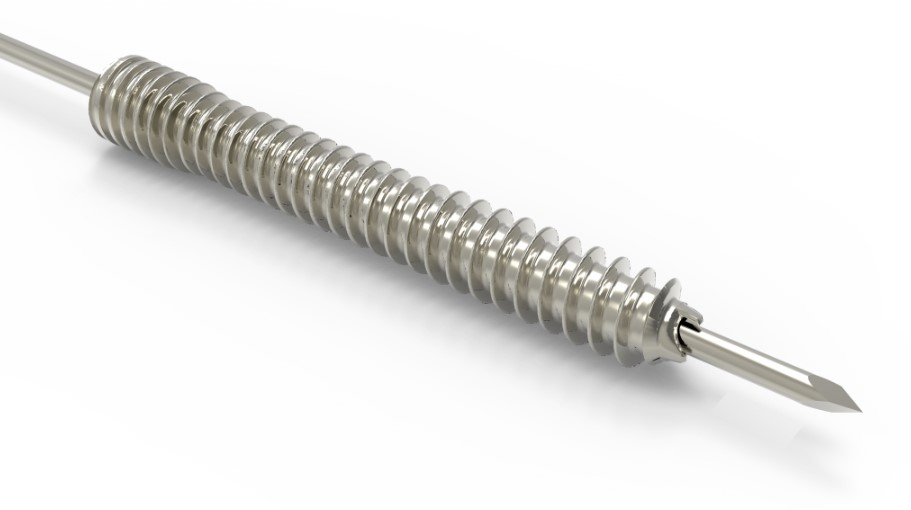
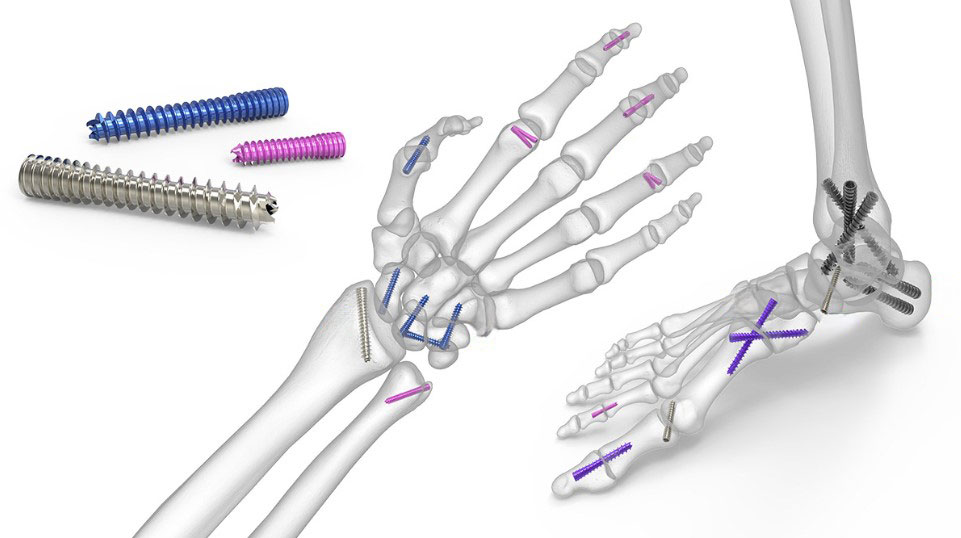
The Acumed Acutrak 2 Headless Compression Screw System is the latest evolution in fully threaded headless screw fixation, with intuitive instrumentation designed to simplify the surgical technique.
The Acutrak 2 System may help minimize drill depth sensitivity and offers 68 unique screw size options to fit a wide variety of applications throughout the body.
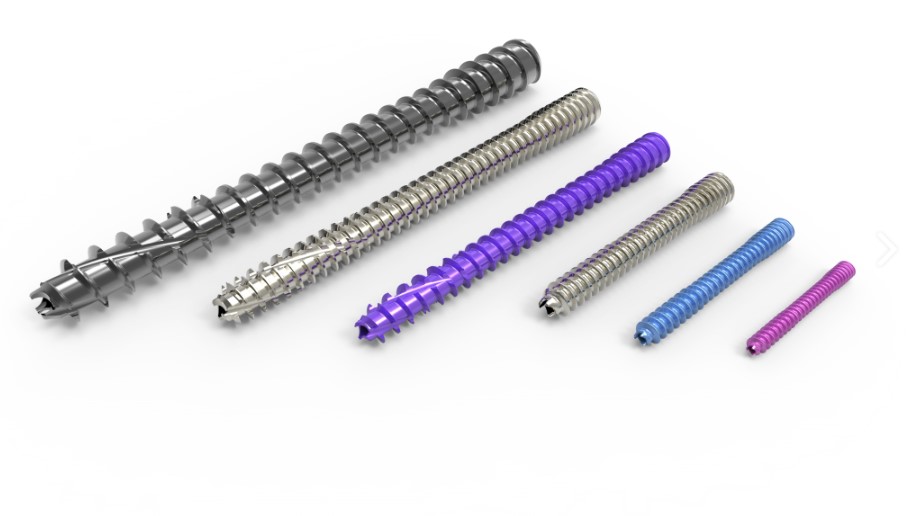
The Acutrak 2 Headless Compression Screw System includes the Acutrak 2 Micro, Acutrak 2 Mini, Acutrak 2 Standard, Acutrak 2 – 4.7, Acutrak 2 – 5.5, Acutrak 2 – 7.5.
The Acutrak Advantage
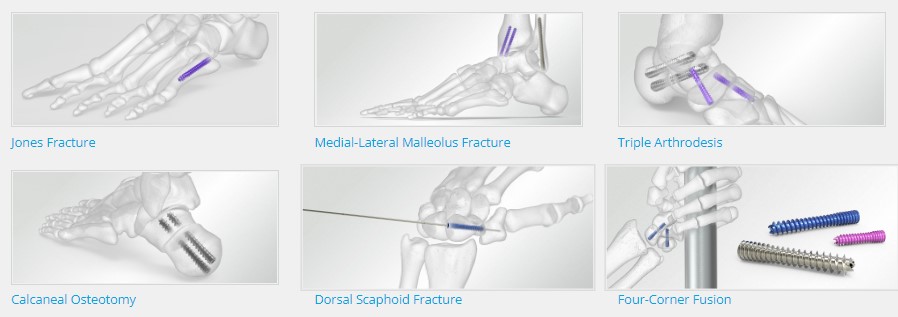
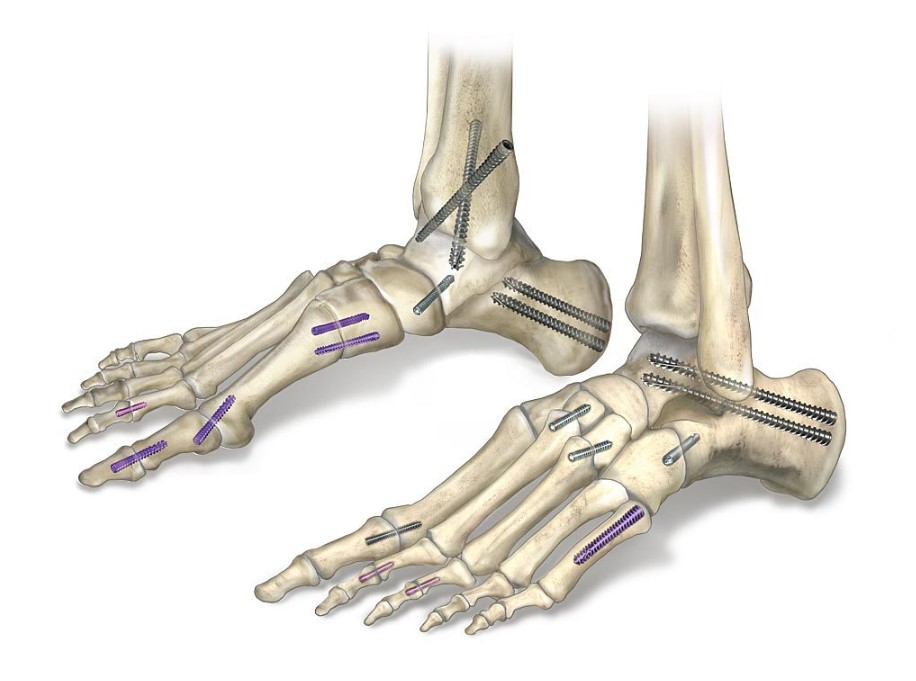
With its introduction in 1994, Acutrak Headless Compression Screw technology revolutionized the way surgeons treat fractures, fusions, and osteotomies. Acutrak 2 introduced the next generation in fully threaded headless fixation, with larger guide wires, larger hex drivers, and a tapered end. The Acutrak 2 System is routinely used in a number of lower-extremity fracture fixations, including those featured below.
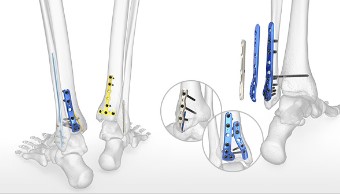
Solutions for Simple to Complex Trimalleolar Injuries
Trimalleolar fractures involve the lateral malleolus, the medial malleolus, and the posterior malleolus. See how Acumed Foot and Ankle products provide solutions to treat these often challenging cases. Watch video, see clinical and biomechanical evidence, and explore case studies.
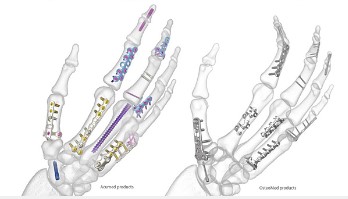
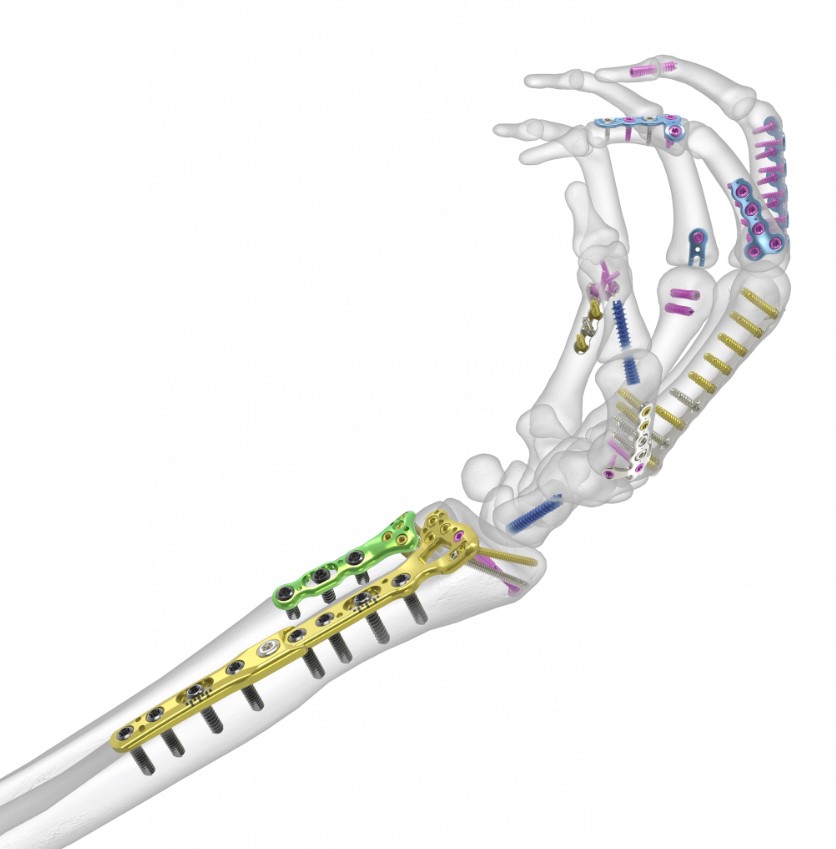
Hand Fracture Solutions That Have You Covered
From straightforward to specialized solutions, Acumed l OsteoMed offers a comprehensive portfolio of upper extremity fixation and specialty plates.
Features
1. Wheeler DL, McLoughlin SW. Biomechanical assessment of compression screws. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998;350:237-245.
Continuously Variable Thread Pitch
The Acutrak fully threaded continuously variable thread pitch screw design provides greater compression and a larger window of compression as compared to partially threaded Herbert style screw designs.1 In addition, this feature allows a fracture or osteotomy site to lie almost anywhere along the length of the screw.
A Family of Options
Available in six different families for a total of 68 different screws, addressing applications throughout the upper and lower extremities.
Fully Threaded
Biomechanical studies have shown that fully threaded screws better handle the cyclic loading that may occur during healing. The Acutrak Headless Compression Screw technology has shown greater push-out strength, greater resistance to cyclic loading, and greater resistance to torsional loading when compared to differential pitch screw technology.1
A Heritage of Healing
Over 1.7 million Acutrak family screws implanted since 1994, supported by more than 100 clinical and biomechanical studies.
Wheeler DL, McLoughlin SW. Biomechanical assessment of compression screws. Clin Orthop Rel Res. 1998;350;237-245.
Videos
This animated overview of the Acutrak 2 Headless Compression Screw System illustrates how the system is designed to treat fractures, fusions, and osteotomies of the upper and lower extremities.
The Acutrak and Acutrak 2 screws have revolutionized headless fixation with a uniquely patented thread pitch that varies continuously from tip to tail. Each thread engages bones faster than its trailing thread, generating gradual compression along the entire length of the screw.
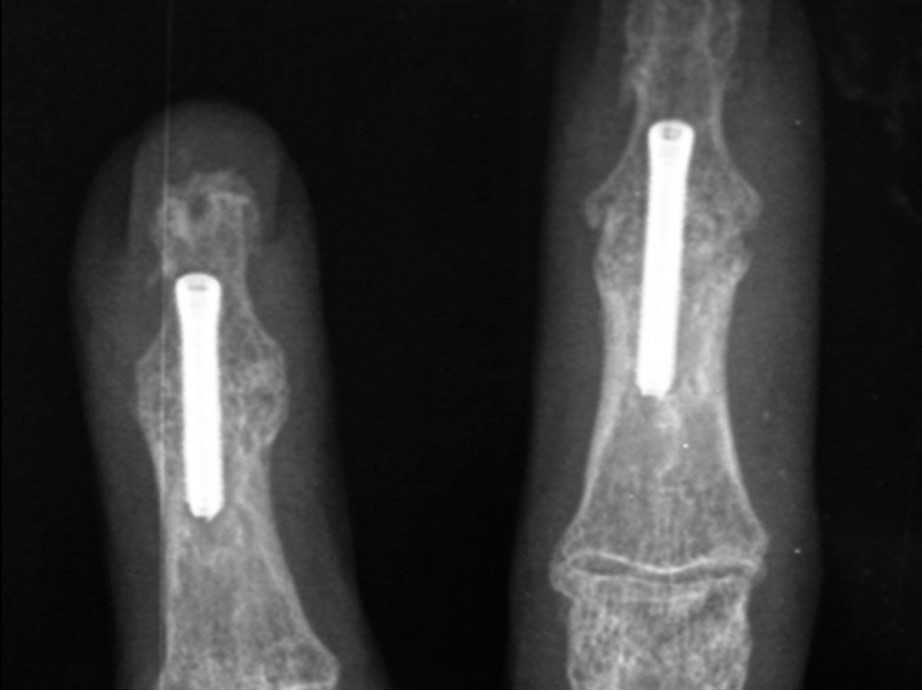
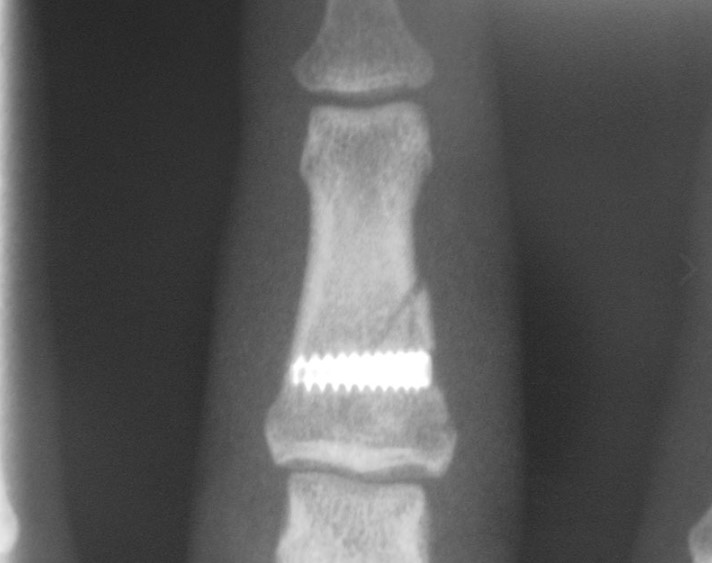
Phalangeal Fixation Animated Surgical Technique
An animated version of Acumed’s suggested surgical technique for Phalangeal fractures using the Acutrak 2 Micro screw to ensure reduction of the fragment, secure the fracture, and maintain rotational stability.
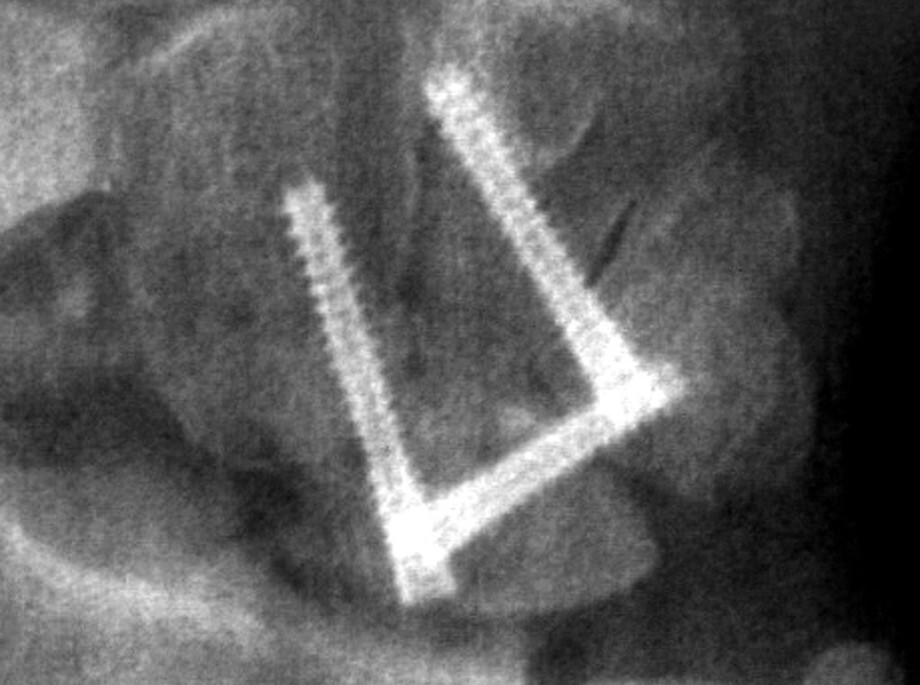
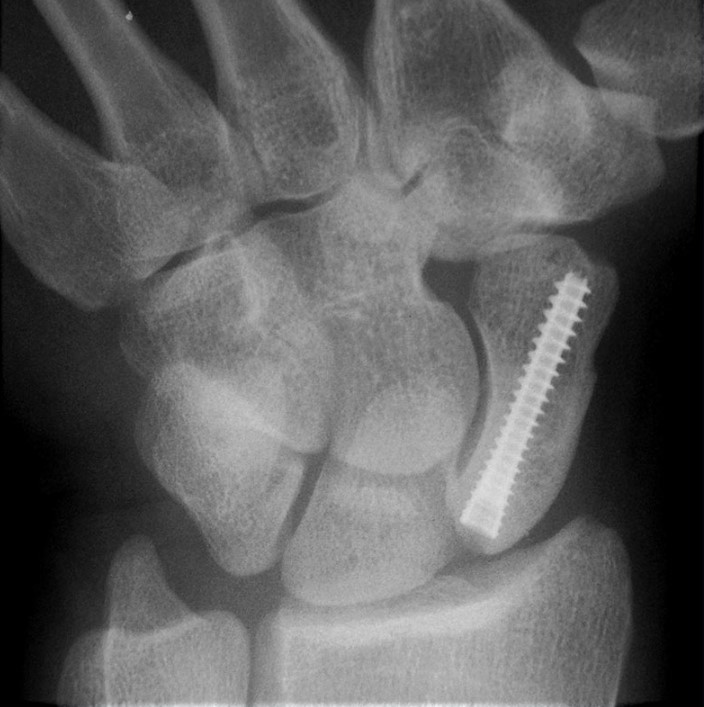
Radial Styloid Fracture Reduction Animated Surgical Technique
Step-by-step animated instructions of Acumed’s recommended surgical procedure using the Acutrak 2 Standard screw to reduce a radial styloid fracture, and secure it in order to maintain reduction and rotational stability.
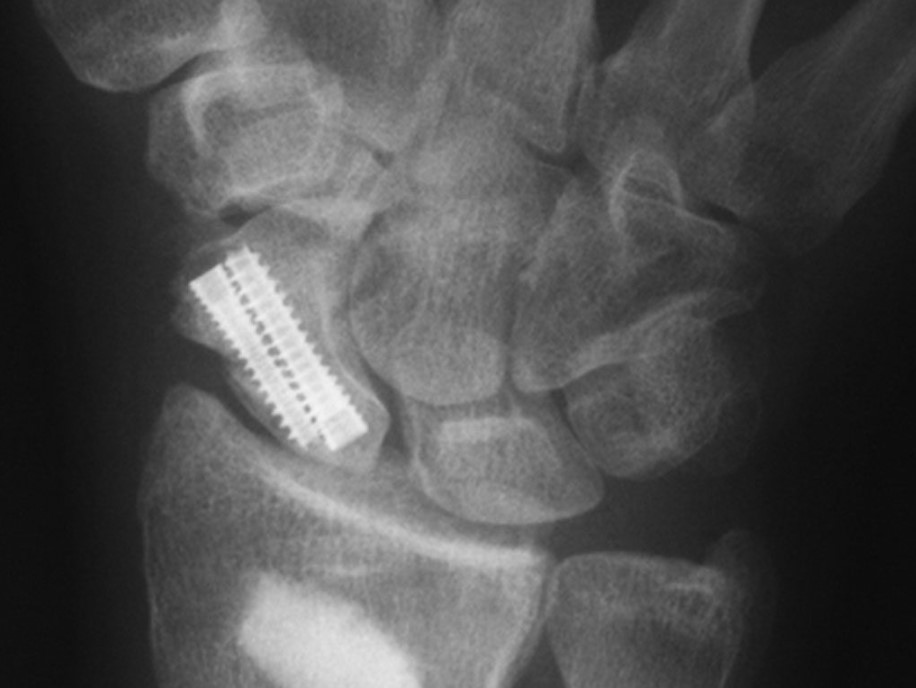
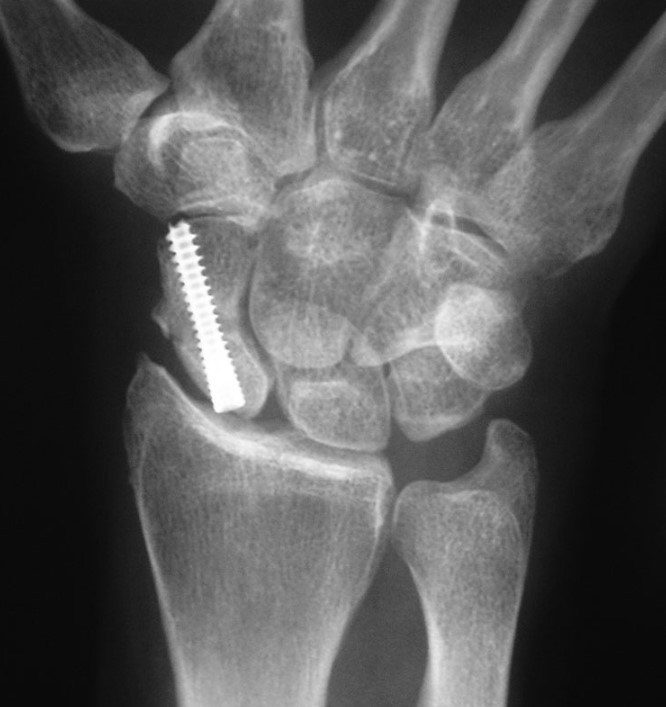
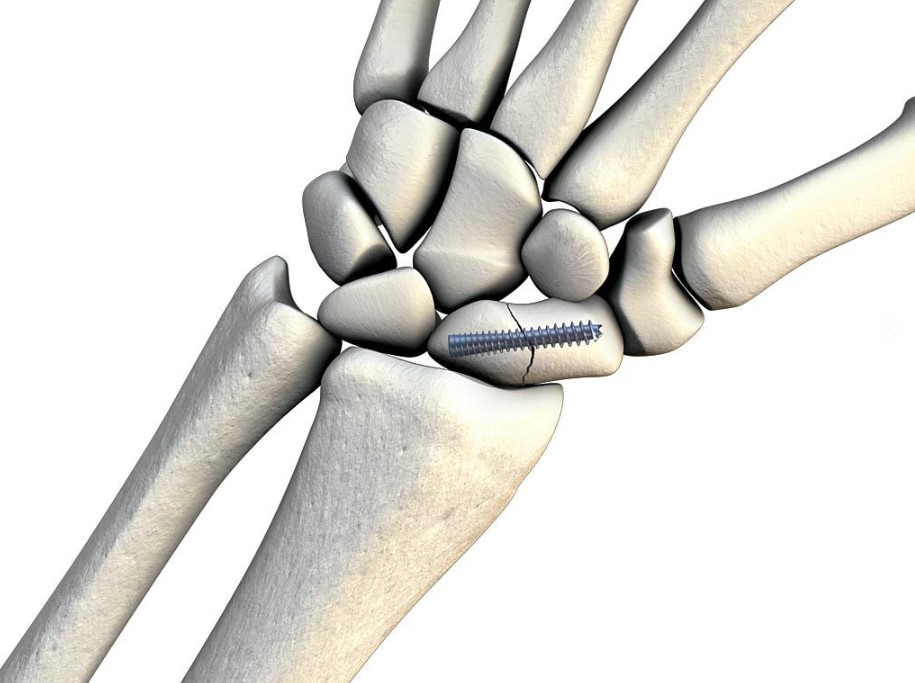
Scaphoid Fracture Reduction Animated Surgical Technique
An animated version of Acumed’s recommended scaphoid fracture surgical technique using the Acutrak 2 Mini Screw to effectively reduce and secure the fractured scaphoid, and maintain rotational stability.
Jones Fracture Reduction Animated Surgical Technique
An animated version of Acumed’s recommended surgical procedure for reducing and fixating fractures of the fifth metatarsal using the Acutrak-4.7 cannulated screw.
The Acutrak 2 Family
The Acumed Acutrak 2 – 7.5 is part of the latest evolution in fully-threaded headless screw fixation. With instrumentation designed to simplify the surgical technique, the Acutrak 2 – 7.5 is composed of 17 unique screw size options to fit a wide variety of applications throughout the body. Indications for the Acutrak 2 – 7.5 include: ankle arthrodesis, triple arthrodesis, talonavicular fusion, calcaneal osteotomy, subtalar fusion, TMT fusion, calcaneocuboid fusion, hindfoot arthrodesis, greater tuberosity fractures, tibial plateau fractures, and femoral condyle fractures. The Acutrak 2 – 7.5 is available in sizes from 40 mm to 120 mm and is inserted using a 4.0 mm hex driver over a .094″ guide wire.
The Acutrak 2 – 5.5 is part of the latest evolution in fully-threaded headless screw fixation. With instrumentation designed to simplify the surgical technique, the Acutrak 2 – 5.5 is composed of 8 unique screw size options to fit a wide variety of applications throughout the body. Indications for the Acutrak 2 – 5.5 include: Jones fractures, distal radius fractures, talus fractures, malleolar fractures, midfoot fusions, MTP fusions, greater tuberosity fractures, carpal fusions, radial styloid fractures, MCP fusions, capitellum fractures, tarsal fractures, midfoot fusions, OCD repair, and osteotomies. The Acutrak 2 – 5.5 screws are available in lengths up to 60 mm and inserted with a 3.0 mm hex driver over a .062″ guide wire.
The Acutrak 2 – 4.7 is part of the latest evolution in fully-threaded headless screw fixation. With instrumentation designed to simplify the surgical technique, the Acutrak 2 – 4.7 is composed of 10 unique screw size options to fit a wide variety of applications throughout the body. Indications for the Acutrak 2 – 4.7 include: Jones fractures, distal radius fractures, talus fractures, malleolar fractures, midfoot fusions, MTP fusions, greater tuberosity fractures, scaphoid fractures, and nonunions, carpal fusions, radial styloid fractures, MCP fusions, capitellum fractures, tarsal fractures, midfoot fusions, OCD repair, and osteotomies. The Acutrak 2 – 4.7 are available in lengths up to 50 mm, are inserted with a 3.0 mm hex over a .062″ guide wire and are color-coded for easy identification in the surgery room.
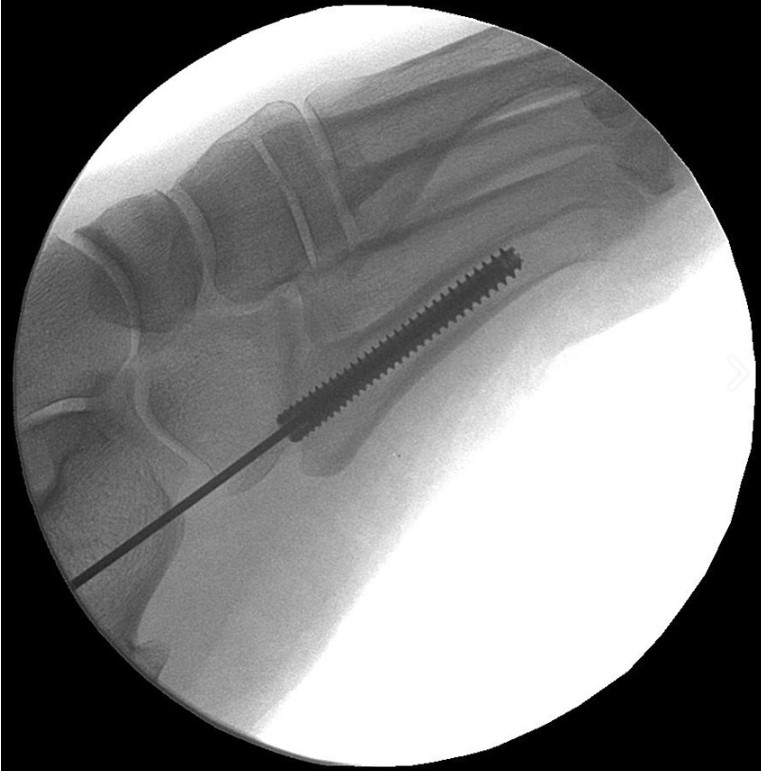
The Acutrak 2 Standard is designed for the fixation of small bone fractures and joint fusions, where a 3.5 mm – 4.0 mm headed screw or an equivalent-sized headless screw would otherwise be required. The Acutrak 2 Standard is extremely versatile, with a variable thread pitch and fully-threaded length that can provide excellent compression for the patient. The Acutrak 2 is indicated for: scaphoid fractures and nonunions, capitellum fractures, navicular fractures, bunionectomies, 5th metatarsal fractures, carpal fusions, and MCP fusions. Acutrak 2 Standard screws are inserted with a 2.5 mm hex driver over a .054″ guide wire.
The Acumed Acutrak 2 Mini incorporates the same design principles as the rest of the Acutrak 2 family of screws, with a smaller diameter and shorter lengths. The Acutrak 2 Mini is designed for the fixation of small bone fractures and joint fusions, where a 3.5 mm – 4.0 mm headed screw or an equivalent-sized headless screw would otherwise be required. Indications for the Acutrak 2 Mini include: scaphoid fractures and nonunions, bunionectomies, radial styloid fractures, radial head fractures, avulsion fractures, carpal fusions, MCP fusions, OCD repair, and Phalangeal fractures. Acutrak 2 Mini screws are available in lengths up to 30 mm, are inserted with a 2.0 mm hex over a .045″ guide wire and are color-coded for easy identification in the surgery room.
The Acutrak 2 Micro incorporates the same design principles as the rest of the Acutrak 2 family of screws. The Acutrak 2 Micro is designed for the fixation of small bones and fracture fragments, where a 2.0 mm – 2.4 mm headed cruciform screw or an equivalent-sized headless screw would otherwise be required. Indications for the Acutrak 2 Micro include: radial head fractures, phalangeal fractures, carpal fractures, metacarpal head fractures, proximal pole scaphoid fractures. Acutrak 2 Micro screws are available in lengths up to 30 mm, are inserted with a 1.5 mm hex over a .035″ guide wire and are color-coded for easy identification in the surgery room.
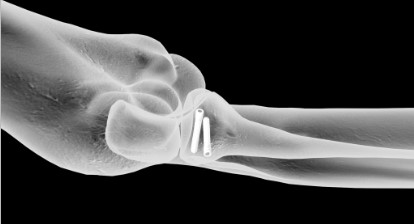
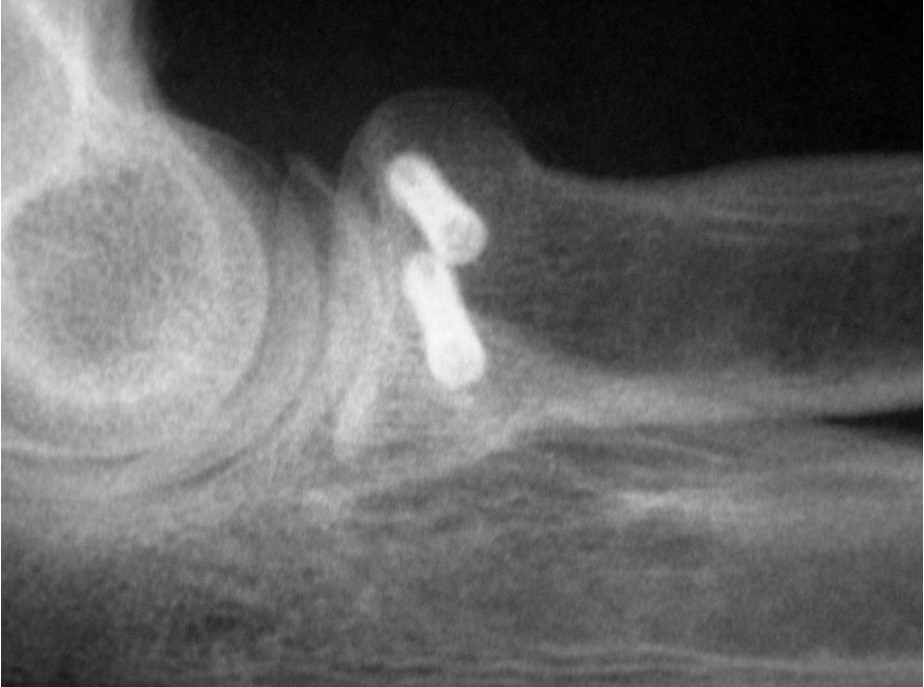
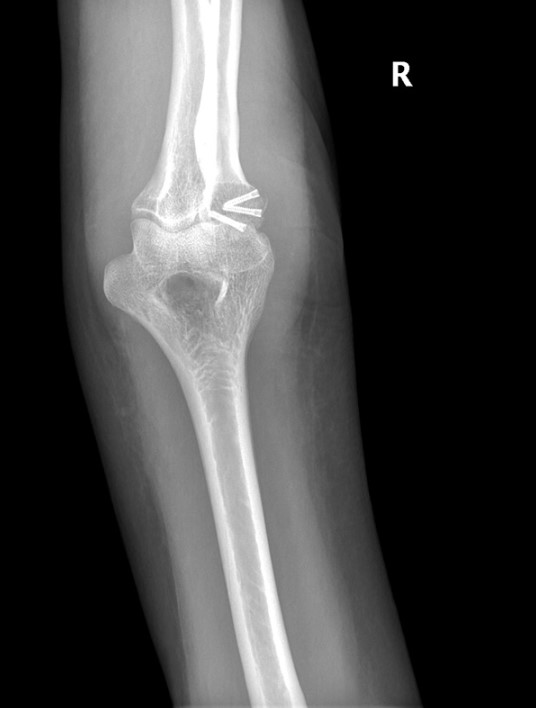
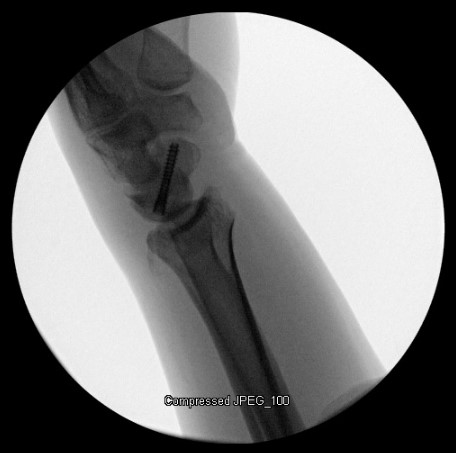
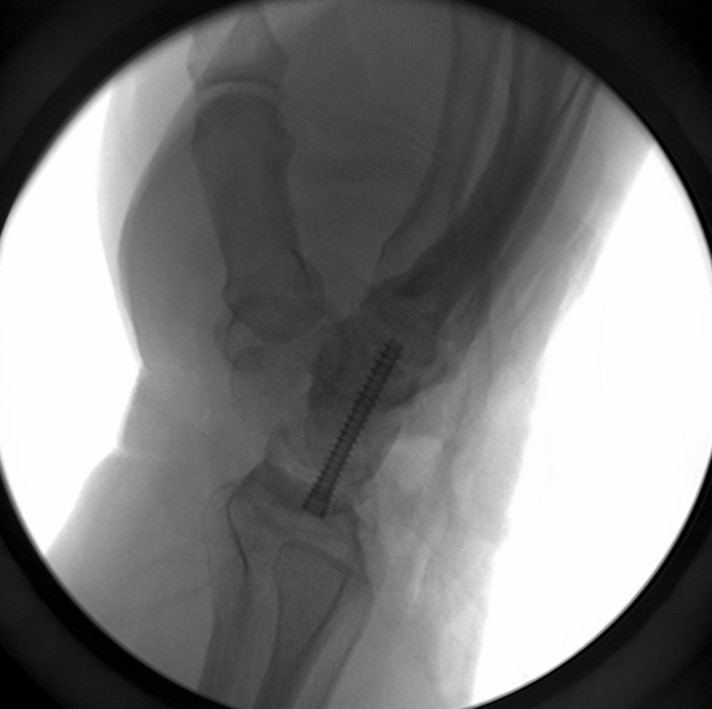
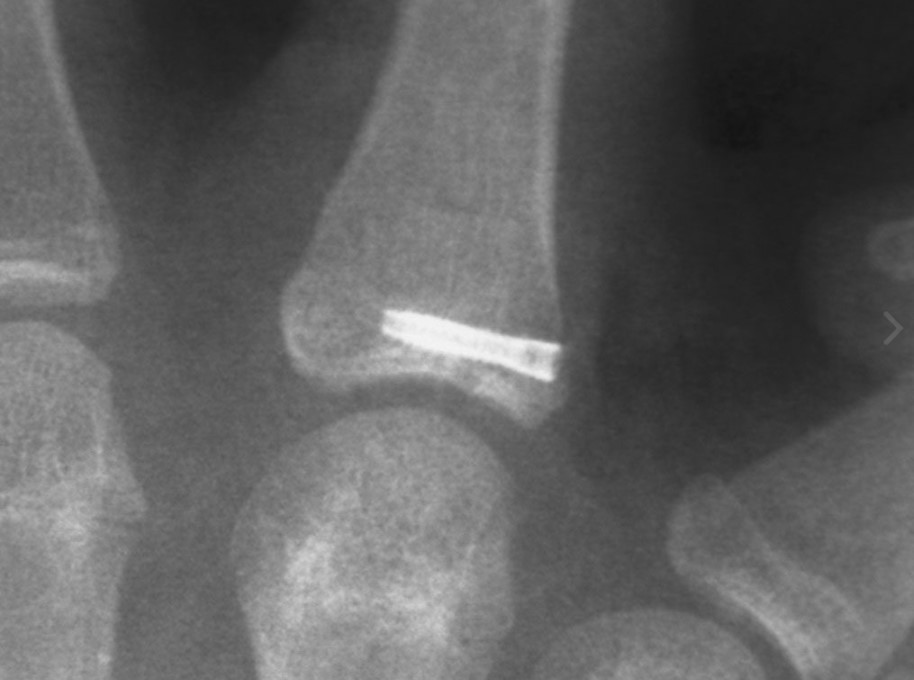
Case Study: Acute Radial Head Fracture
Richard S. Moore, M.D., uses the Acutrak 2 Micro Screws to treat an acute right radial head fracture in a 64-year-old woman following a mechanical fall onto an outstretched hand. Who complained of pain and limited range of motion of the elbow.
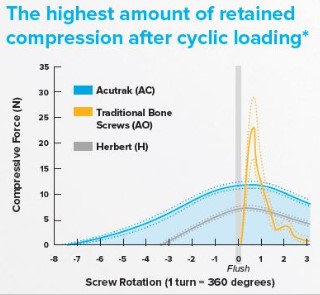
Cyclic Loading
The highest amount of retained compression after cyclic loading1.The highest resistance to torsional loading compared to AO and Herbert screws in cadaveric and synthetic bone material.1
1. Wheeler DL, McLoughlin SW. Biomechanical assessment of compression screws. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998;350:237-245.
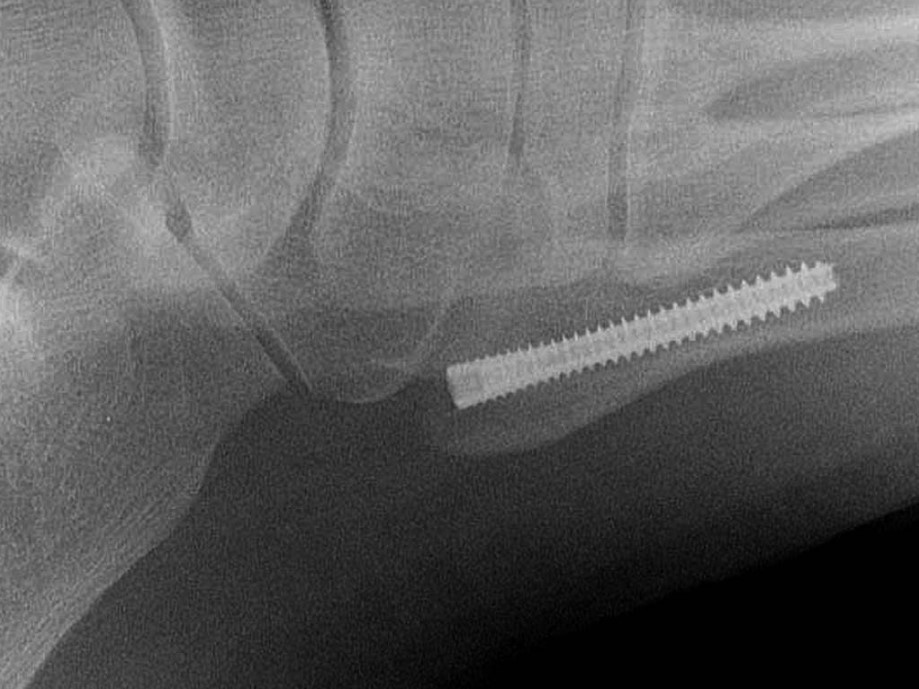
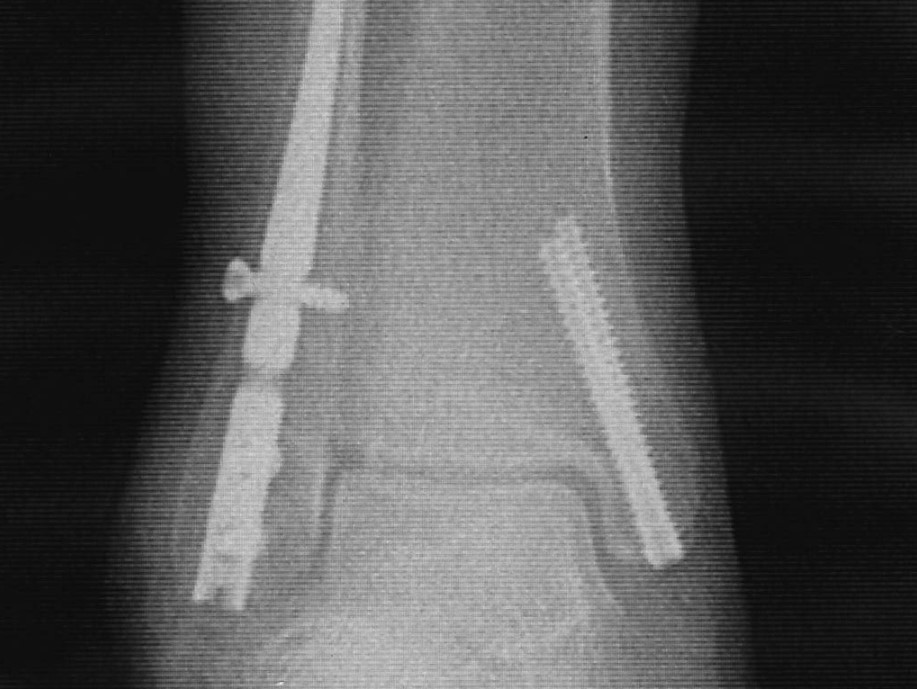
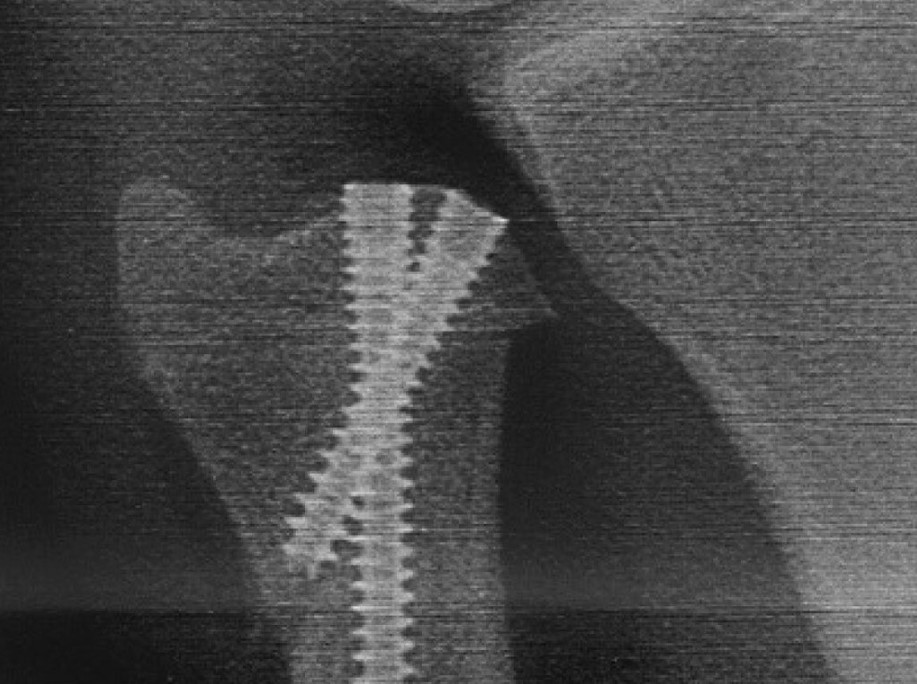
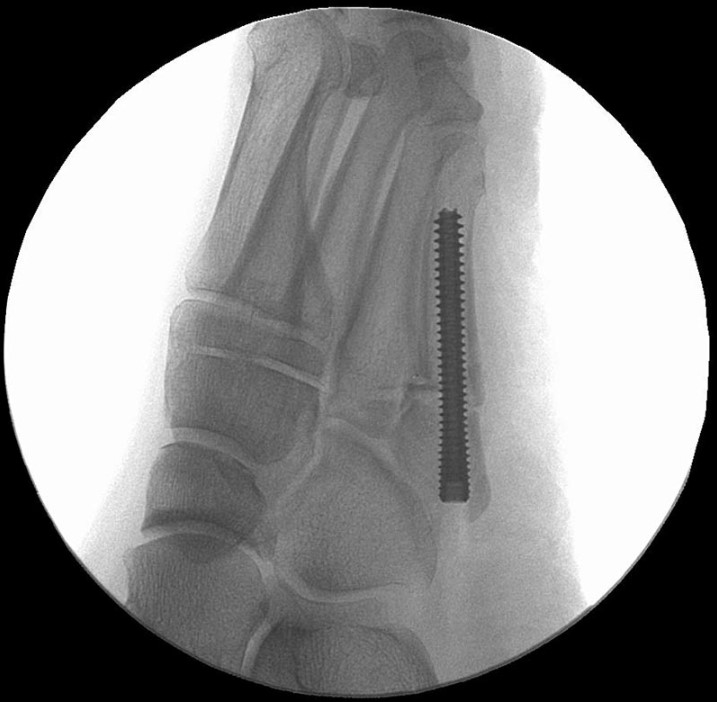
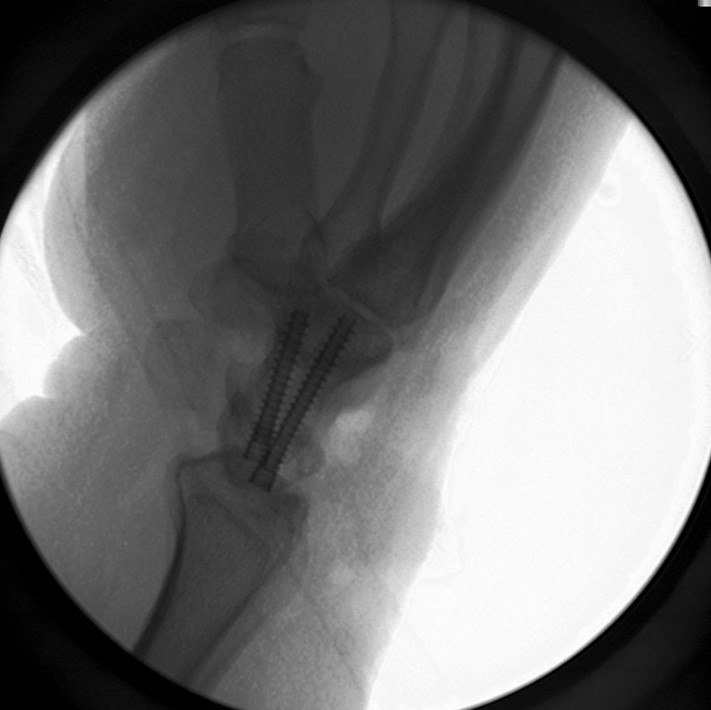
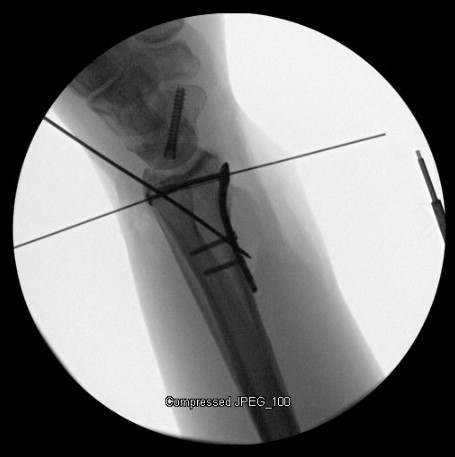
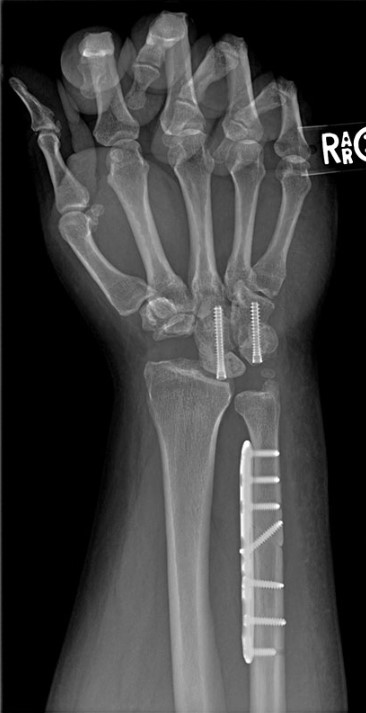
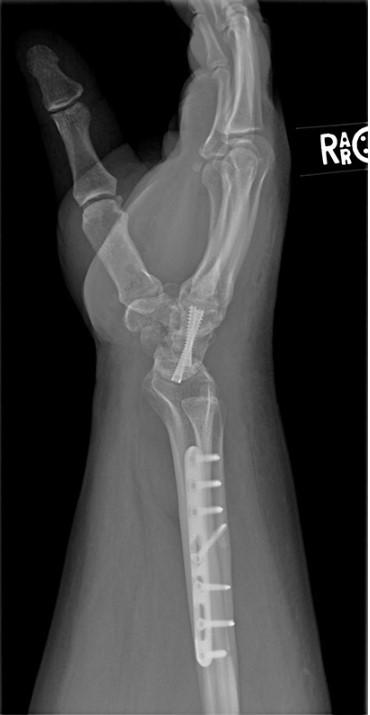
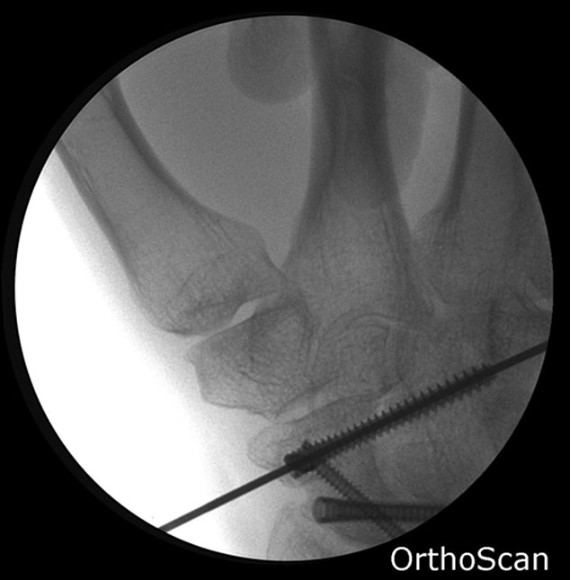
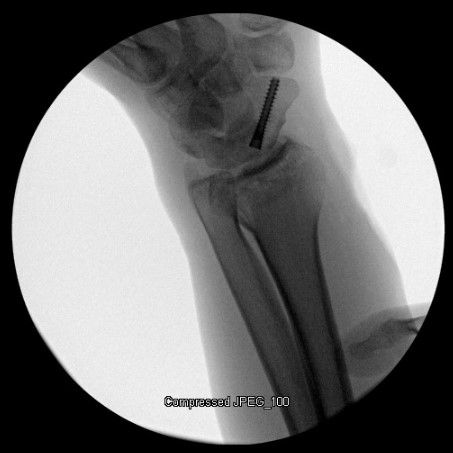
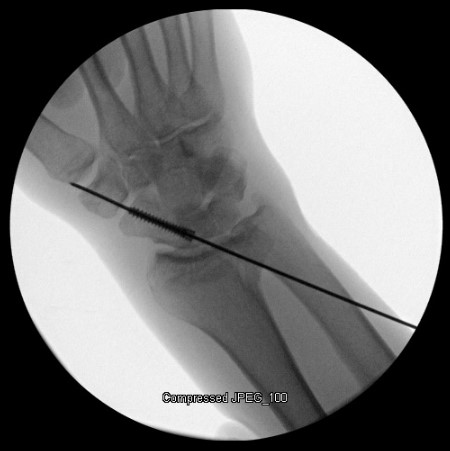
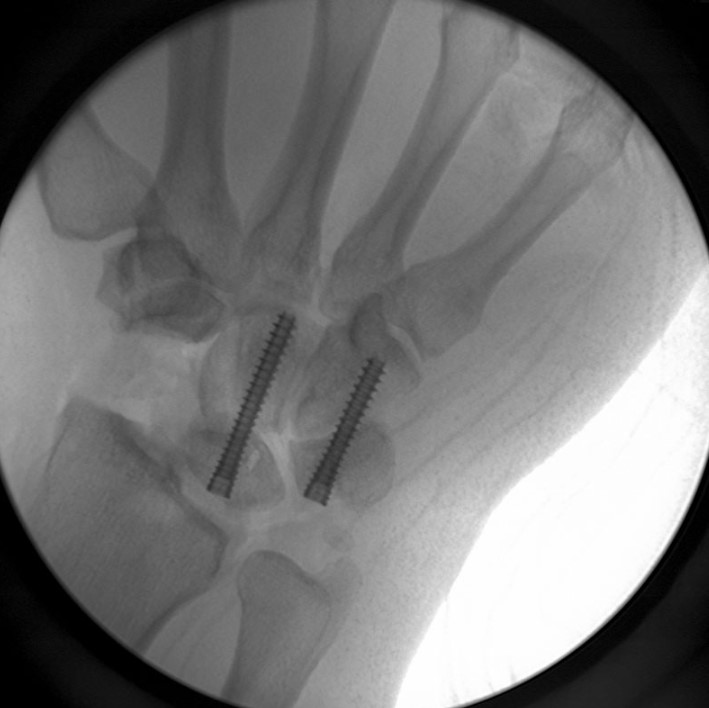
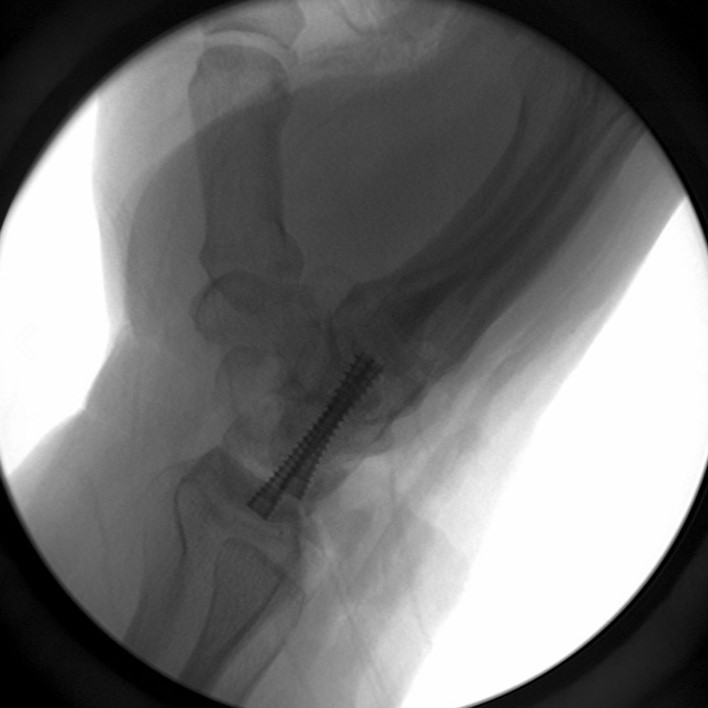
Image Gallery
Info Contact
| HEAD | OFFICE |
| Tel | +27 (11) 966 0600 |
| info@medhold.co.za | |
| Address | MSI Business Park, 68 Rigger Road, Spartan, Kempton Park, Gauteng, 1619 |