Forearm Fracture Solutions Surgical Technique
Forearm Fracture Solutions Hand Wrist – Fixation Products
Forearm Fracture Solutions
Product Overview
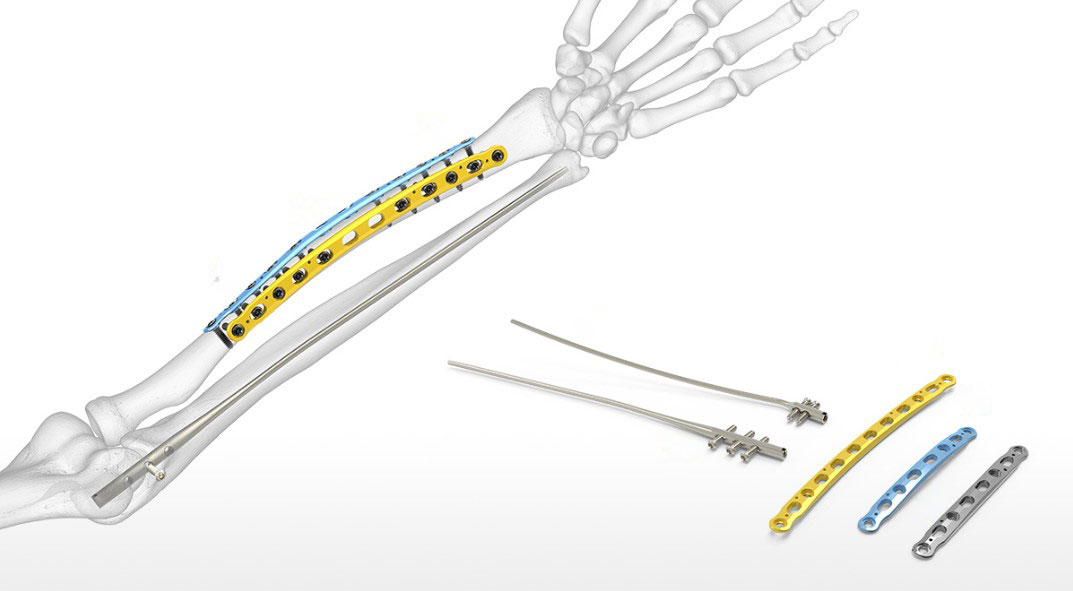
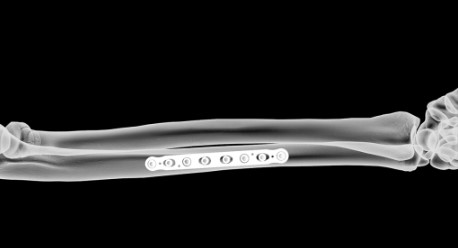
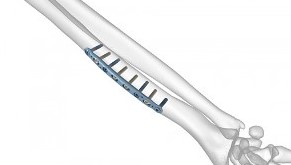
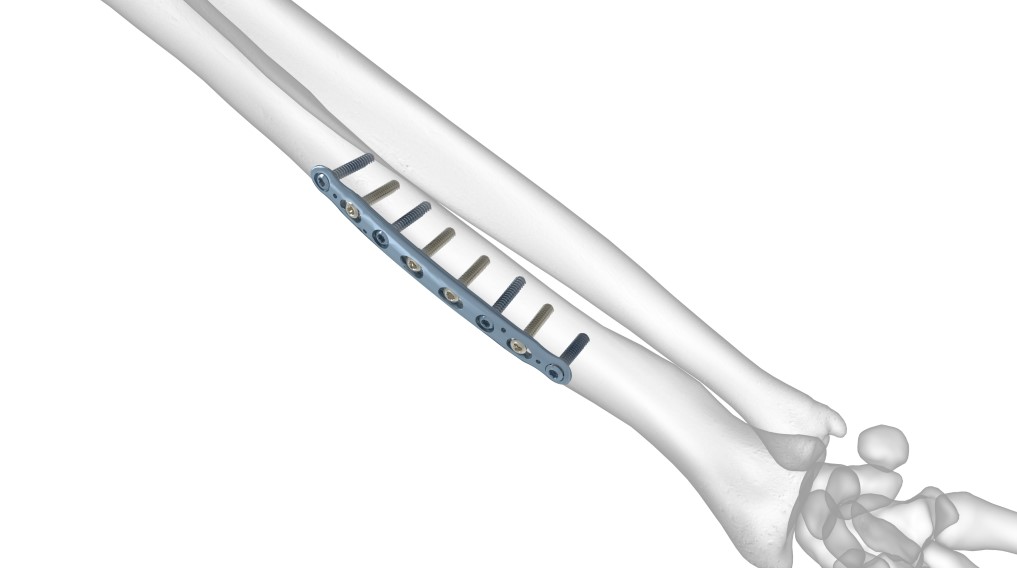
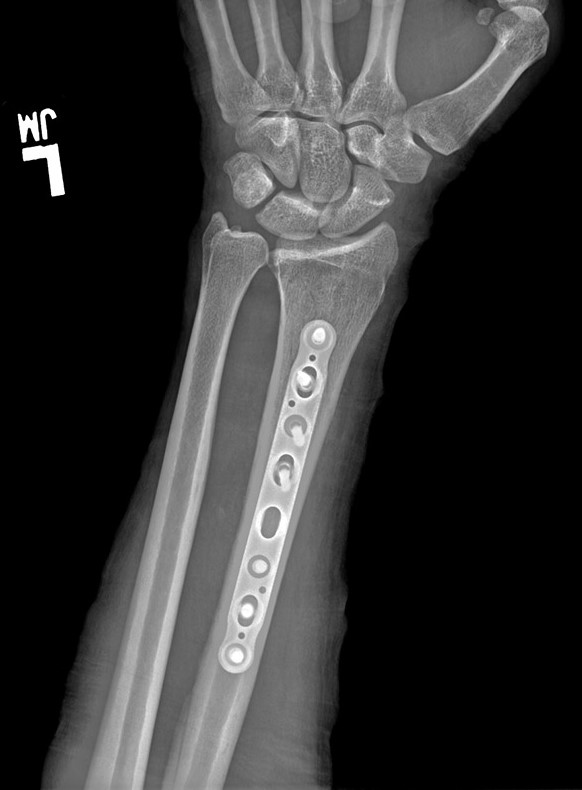
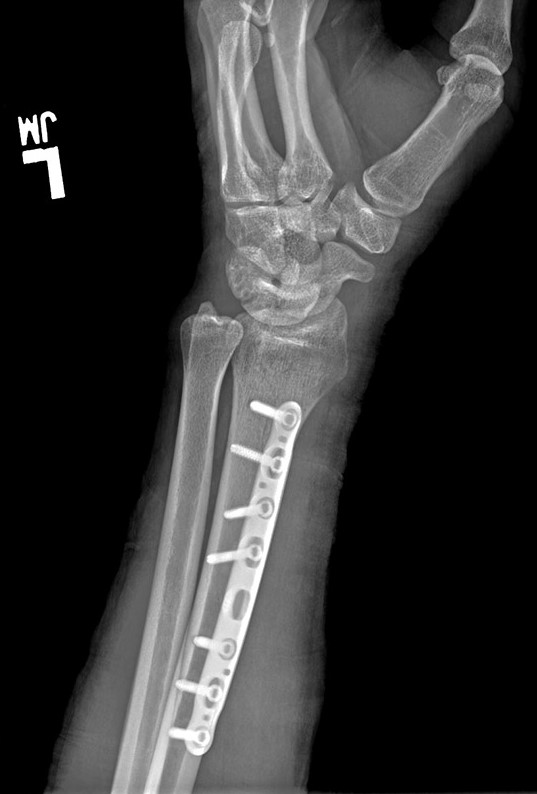
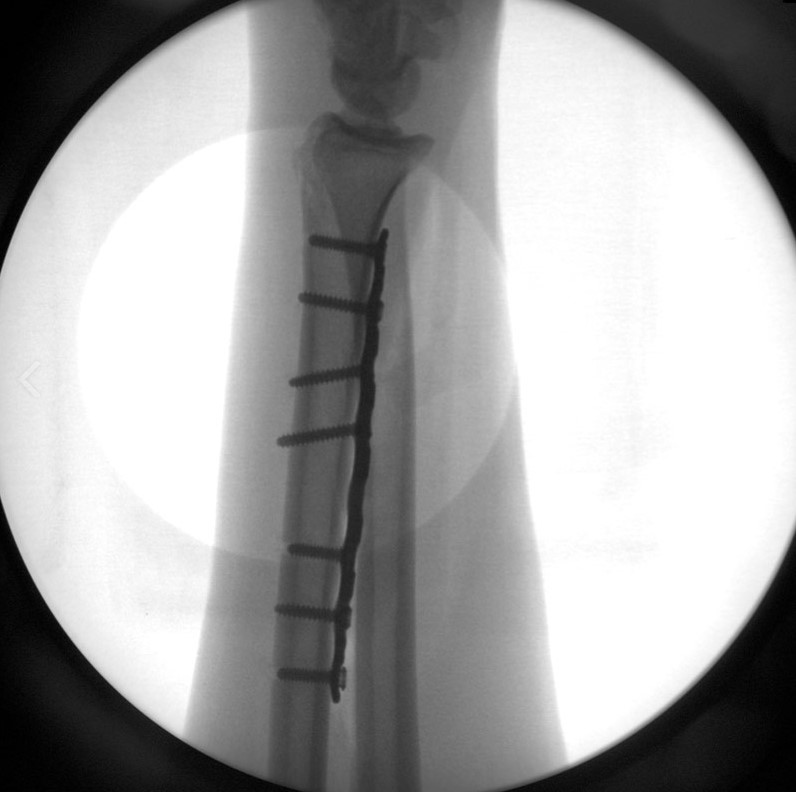
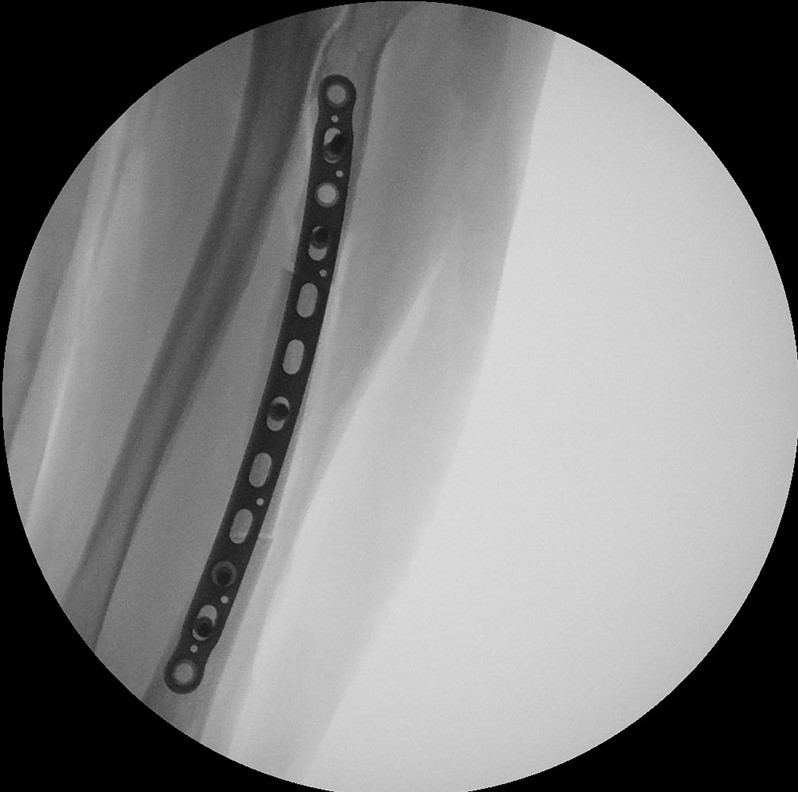
The precontoured radius plates of the Acumed Anatomic Midshaft Forearm Plating System offer marked hardware improvements over traditional straight plates. The system can be used to treat fractures, fusions, and osteotomies of the radius and ulna. It can also be used in conjunction with the Acumed Forearm Rod System for a less invasive approach to radius, ulna, and both-bone forearm fractures in the diaphyseal region. The Anatomic Midshaft Forearm Plating System includes Midshaft Ulna Plates, Volar Midshaft Radius Plates, and Dorsolateral Midshaft Radius Plates.
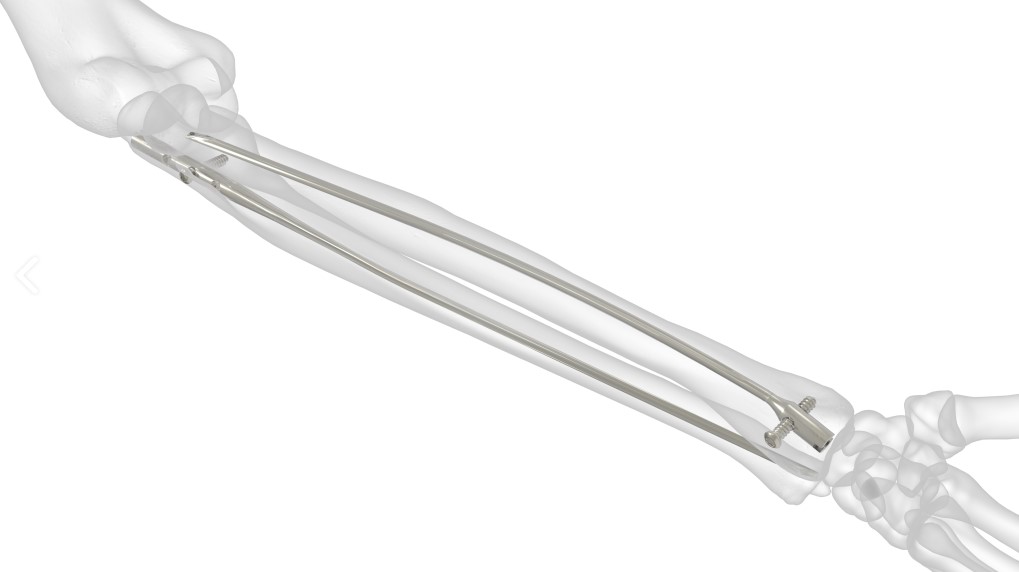
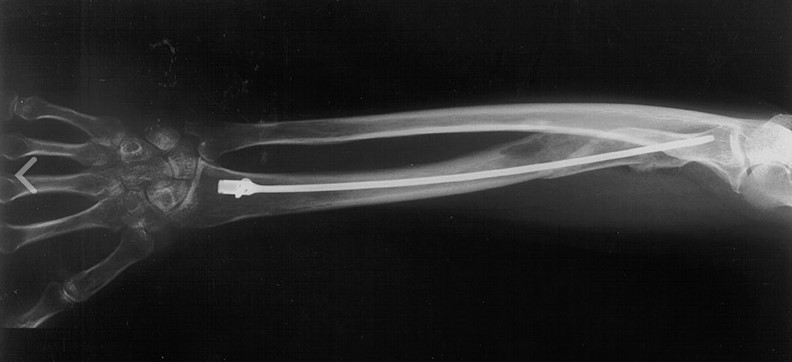
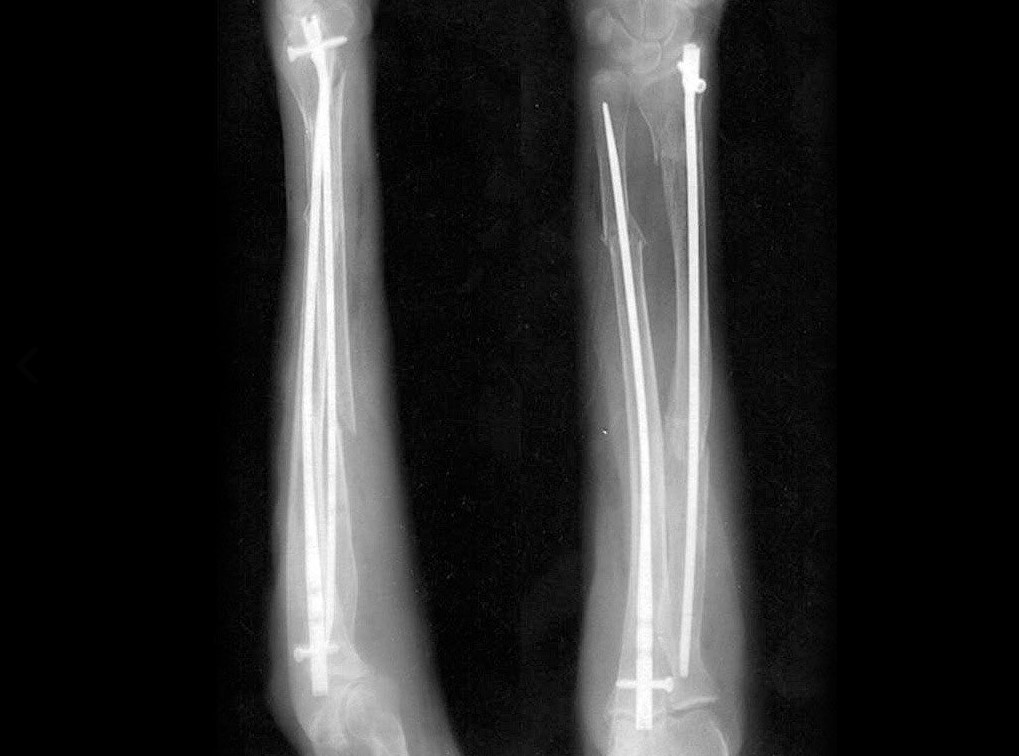
The Acumed Forearm Rod System offers surgeons an alternative option for the treatment of fractures and osteotomies of the radius and ulna over traditional plating. Each fluted rod is designed to be inserted through a small incision with minimal canal reaming. A targeted interlocking screw, combined with a paddle blade tip design, locks and rotationally secures the bone segments to assist in fracture union.
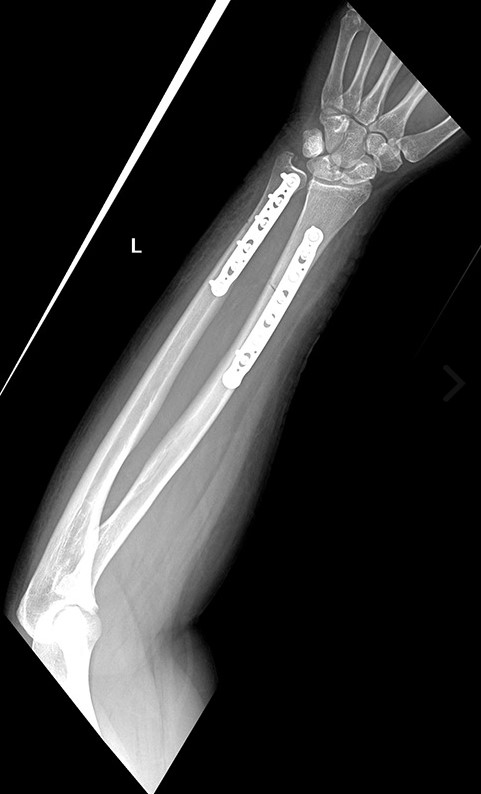
Case Series: Forearm Fractures
In this series of six case studies, Dr. Jared Salinsky uses the Acumed Anatomic Midshaft Forearm Plate System to treat patients with various fractures of the radius and/or ulna including a nonunion of midshaft, a displaced left ulnar fracture, a diaphyseal fracture of the ulna, a grade-2 open fracture, and acute radius and ulna fractures.
Product Training Series: Forearm Fracture System Key Features with Victoria Lauren
Plate Features
The First Precontoured Radius Plates
Due to the sagittal bow of the radius, plating with contoured plates in the sagittal plane improves rotation when compared with straight plates.2 For every 5 degrees of radial curvature that is not restored, the patient may lose 15 degrees of rotational motion.2
Two Contoured Radius Plate Options
Acumed offers two contoured radius plate options, including volar and dorsolateral approach options and an ulna plate.
Precontoured Plate Advantages
Precontoured plates are intended to minimize plate bending to help save operating time. This allows surgeons to focus on restoring anatomy and re-establishing forearm pronation-supination.1
Plate Design Features
Tapered plate ends may reduce stress on bone and risk of secondary or subsequent fracture adjacent to the plate. A limited-contact under-surface minimizes contact with the periosteum to avoid disruption of blood supply.
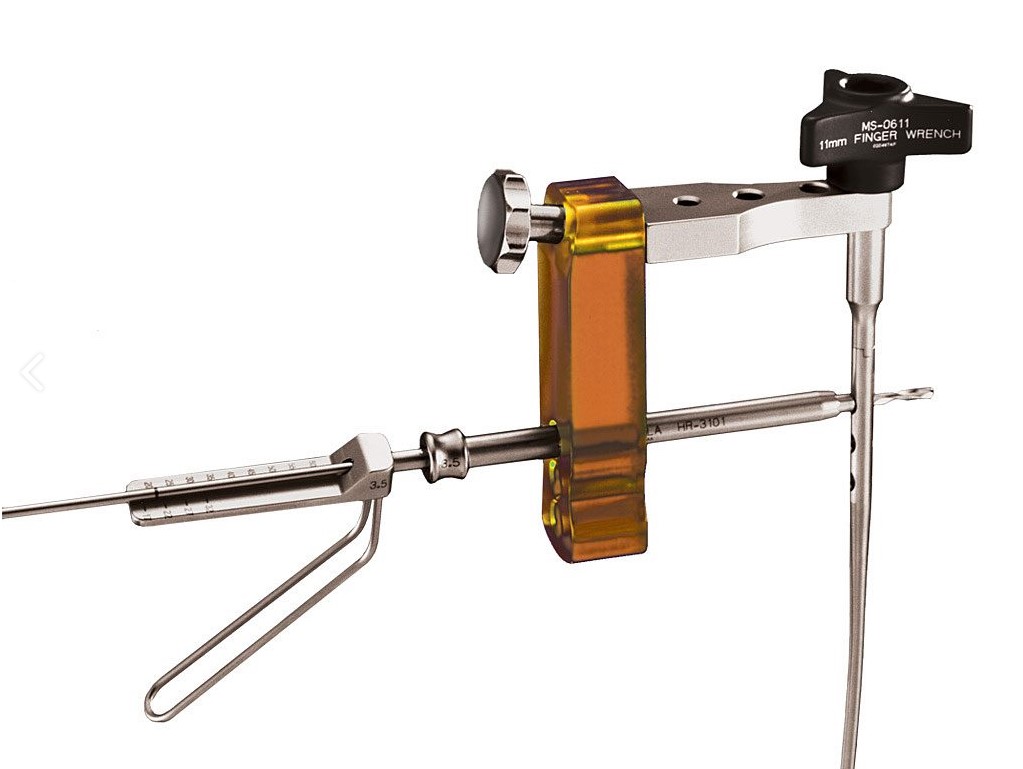
Creative Instrumentation
Innovative instrumentation includes a swiveling plate clamp, an angled drill guide, and a soft tissue spreader to aid in plate implantation.
Rod Features
Minimally Invasive
The rod is designed to be inserted through a small incision with minimal canal reaming.
Rotational Stability
The rod’s paddle-blade tip and interlocking screws are designed to lock and rotationally secure bone segments to assist in fracture union.
Straightforward Technique
The straightforward surgical technique is designed to streamline the surgical experience.
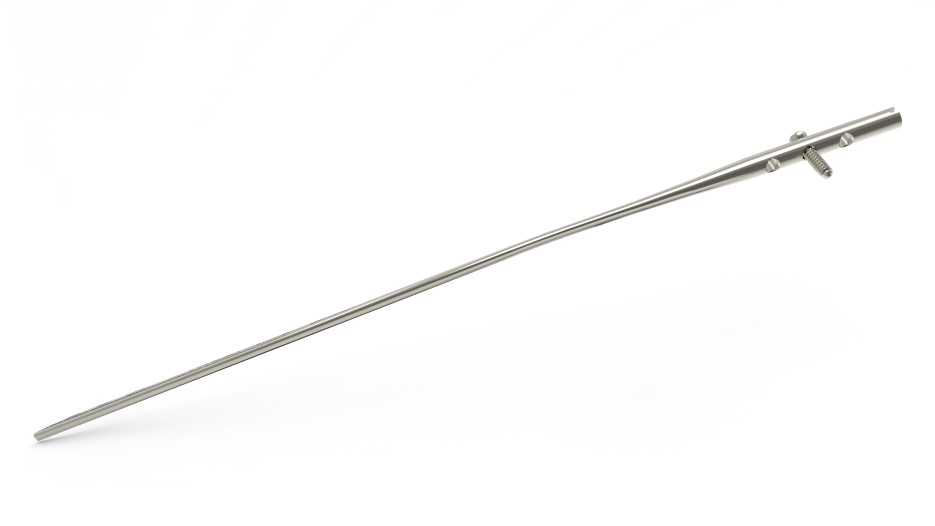
Precontoured Rods
Rods are precontoured to match the ulnar and radial canal’s geometry.
Anatomic Midshaft Forearm Plates
Forearm Rod System
Ulna Rod
The Acumed Ulna Rod is designed to address simple, transverse, and short oblique fractures as well as osteotomies of the ulna. Each fluted rod is designed to be inserted through a small incision with minimal canal reaming. A targeted interlocking screw, combined with a paddle blade tip design, locks and rotationally secures the bone segments to assist in fracture union.
Radius Rod
The Acumed Radius Rod is used to treat fractures and osteotomies of the radius. Contoured to ease insertion and closely match the geometry of the radial canal, the rod’s targeted interlocking screws and paddle-blade tip are designed to lock and rotationally secure bone segments to stabilize the fracture. This minimally invasive technique may reduce scarring and surgery time over traditional open reduction internal fixation (ORIF).
Gallery
Info Contact
| HEAD | OFFICE |
| Tel | +27 (11) 966 0600 |
| info@medhold.co.za | |
| Address | MSI Business Park, 68 Rigger Road, Spartan, Kempton Park, Gauteng, 1619 |